How to Find & Hide Your IP Address
HighSpeedOptions prides itself on providing honest, quality content. While we may be compensated when you make a purchase through links on our site, all opinions are our own. Here's how we make money.
Table of Contents
Finding your IP address is a straightforward process. Protecting it, on the other hand, requires a few extra steps. Here we walk through how to find and hide your IP address so you can maintain your privacy while surfing the web.
Key Takeaways: Finding and Hiding Your IP Address
- IP addresses identify your device online and can reveal your location, ISP, and browsing activity.
- There are two main types of IPs: IPv4 (numeric, older, limited supply) and IPv6 (alphanumeric, designed for growth). Most users also have dynamic IPs that change periodically.
- Finding your IP is simple — you can use a browser search, run a speed test, or check directly in system settings on Mac or Windows.
- Hiding your IP improves privacy, security, and access by protecting against hackers, avoiding tracking, bypassing geo-restrictions, and reducing censorship risks.
- Common methods to hide your IP include VPNs, proxies, Tor, public Wi-Fi, and mobile data — each with pros and cons.
- Drawbacks exist: slower speeds, blocked services, occasional disconnections, and risks from shady or restricted tools.
- Real-world uses include streaming abroad, safe browsing on public Wi-Fi, avoiding price discrimination, protecting identity while gaming, and accessing blocked sites.
- Legality varies: IP masking is legal in most countries, but restricted in places with heavy censorship. Always use tools responsibly and within the law.
- Best first step for most people: a reputable VPN, paired with secure browsing habits and strong cybersecurity practices.
What is an IP Address?
An IP address is a unique identifier that allows devices to connect, be recognized, and be located on a network. Your IP address is provided by your internet provider or your network administrator.
Two types of IP Addresses
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) is the older, most frequent form of IP address. It’s a numerical address separated by periods, such as 192.168.1.1. The number of available IPv4 addresses is limited, which is challenging given the growth of the internet and the number of connections.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) was developed to address this issue. IPv6 addresses are alphanumeric and separated by colons (i.e., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334). Clearly, IPv6 accommodates significant growth.
It’s also important to note that there are static and dynamic IP addresses. A static IP address remains the same over time, whereas a dynamic IP address changes every time a device connects to the internet. Most residential internet users have dynamic IP addresses.
Your internet provider is the first step in keeping your data and devices secure.

How Do I Find My IP Address?
You can find your IP address by performing a speed test, using a browser, or checking system settings on a Mac or PC. Follow the steps below to find the IP address on your device.
How to Find Your IP Address Using a Speed Test
One of the easiest ways to find your IP address is to perform an internet speed test. Your address will appear in the results, typically shown alongside your provider name or the name of the nearest server.
How to Find Your IP Address Using a Browser
To access your IP address from your browser, all you have to do is type “what is my IP address” or “how to check my IP address?” into your search engine of choice. Search engines like Google will display your unique IP address at the top of the search results page. You can also visit whatismyip.com, to quickly find your IP address
How to Find Your IP Address on a Mac
- Click the Apple icon at the top left of your screen.
- Select “System Preferences”
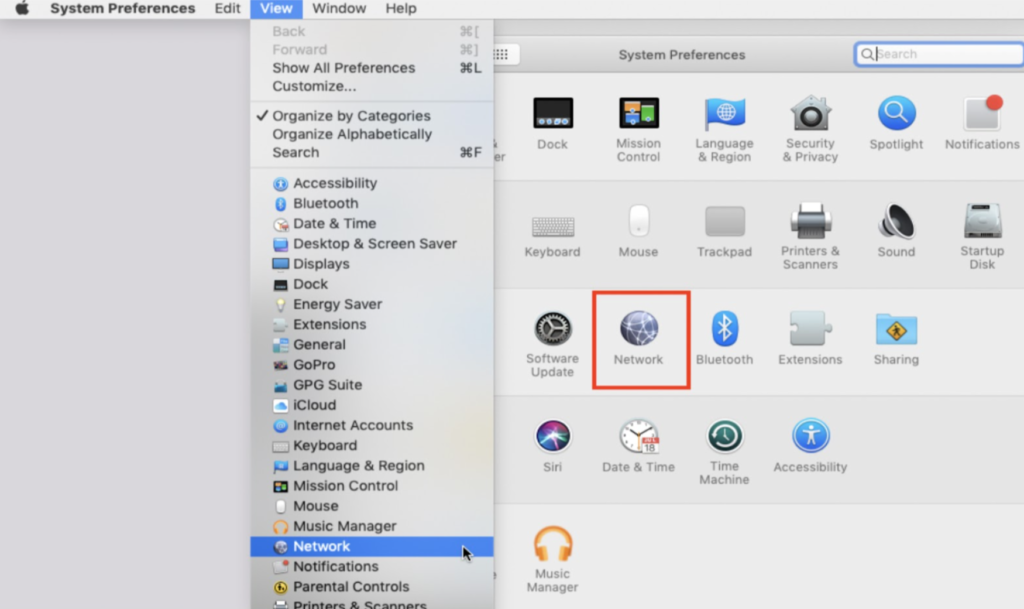
- Scroll to the “View” menu. When you hover your mouse over the View menu, more options will appear—select “Network” from there.
- Click on “Network Connection” in the left column. You will then select either Ethernet or WiFi, depending on how you’re connected to the internet.
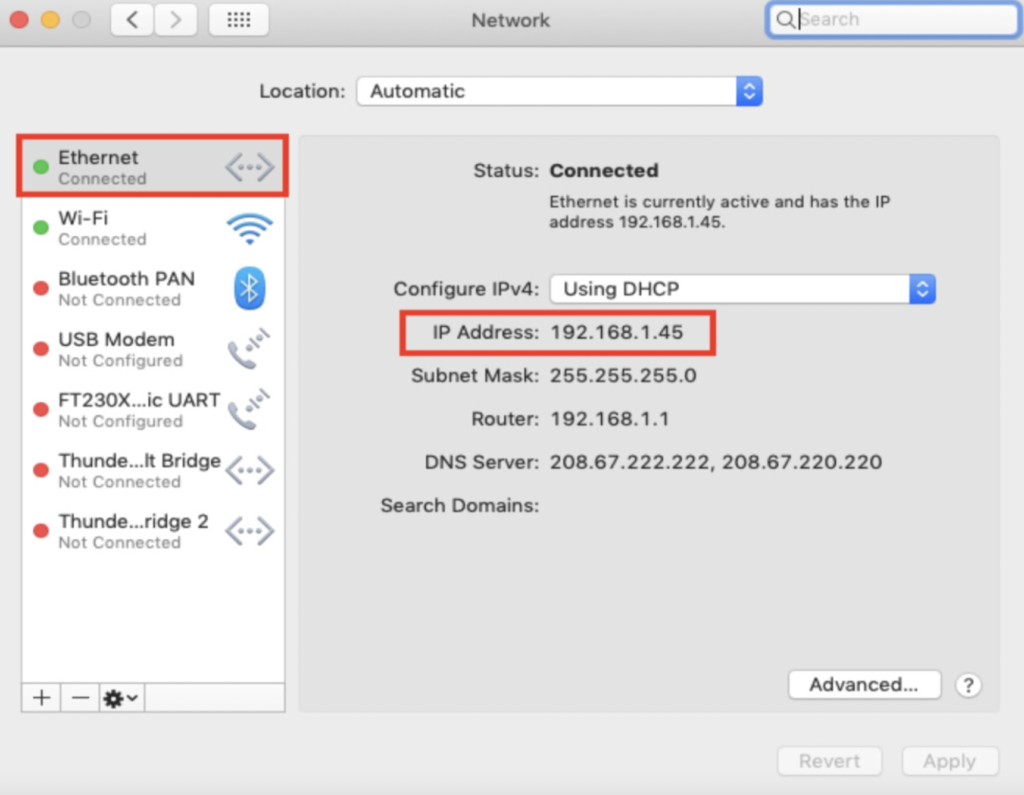
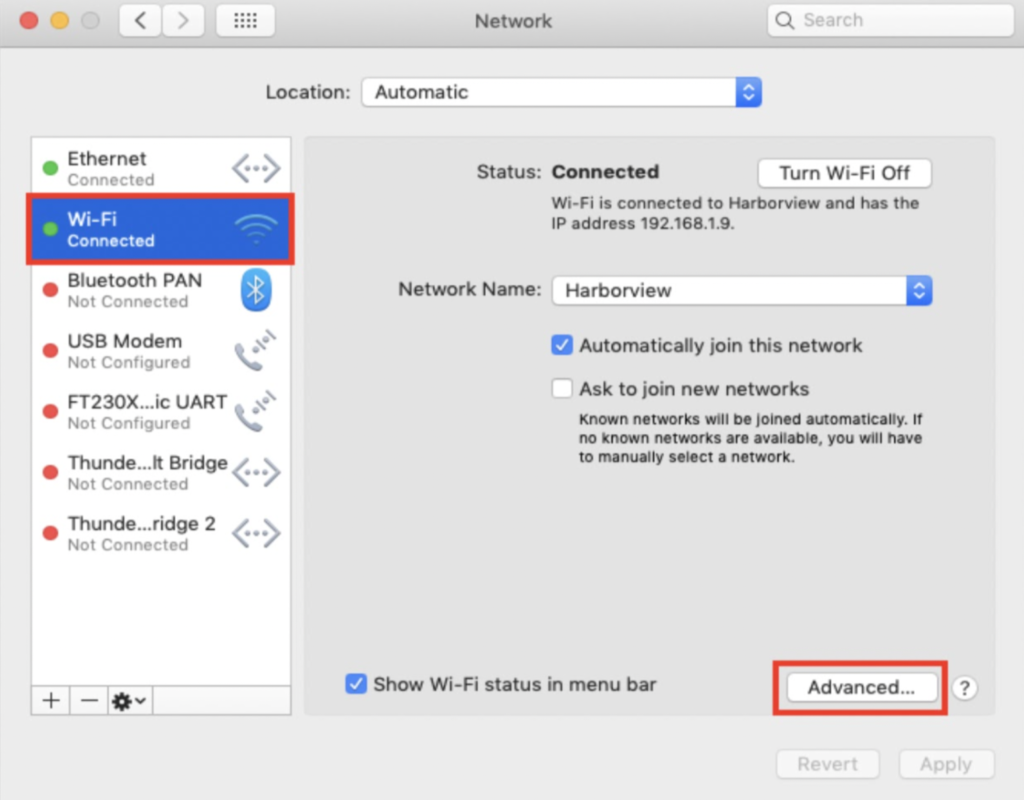
- Your IP address will show up immediately for an Ethernet connection. For a WiFi connection, click the “Advanced” button in the lower right corner. Then, click the “TCP/IP” tab across the top of the window. It will show up there.
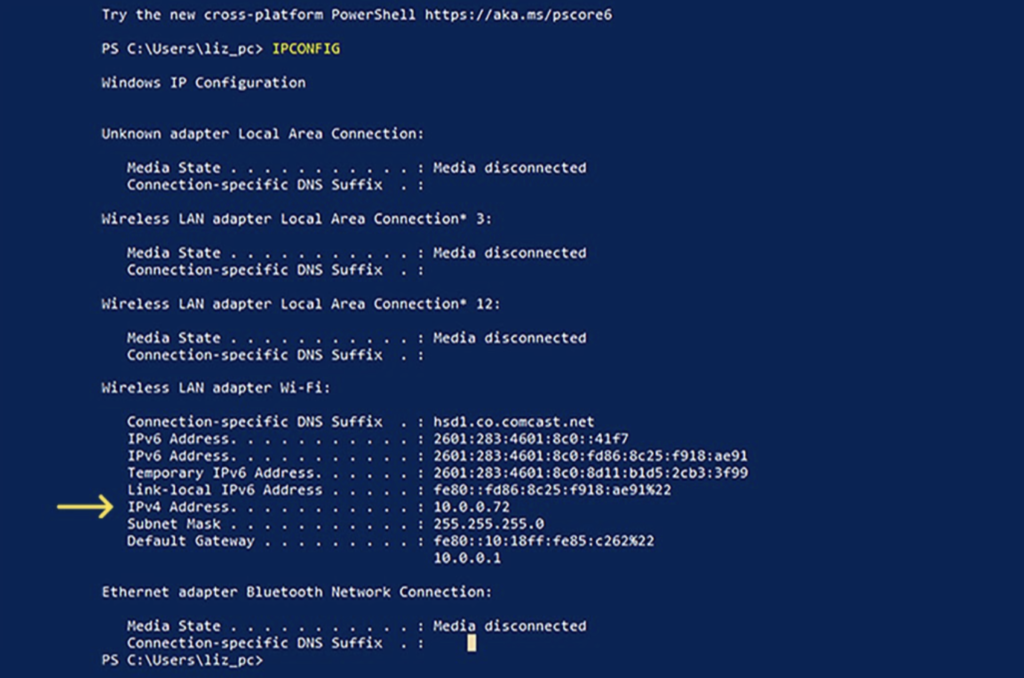
How to Find Your IP Address on Windows
- Right-click on the “Start” button.
- Select “Windows PowerShell” on the Power User Menu.
- Type the command “IPCONFIG” into the Windows PowerShell, press enter, and your IP configuration information will show up.
- Your IP address will be the IPv4 address displayed on the screen.
Why Should I Hide My IP Address?
Leaving your IP address exposed, or unmasked, presents some risks and can limit your online experience. But to be clear, hiding your IP address adds privacy, but it doesn’t make you invisible online. Here are a few reasons why you should hide your IP address:
Boost Online Privacy
Your IP address reveals your rough location and internet provider and can be used by advertisers and websites to target you with ads.
Enhance Your Security
Hackers and cybercriminals can exploit IP addresses to gain unauthorized access to your system, install malicious software, or steal personal information.
Bypass Geo-restrictions
Many online services, like streaming platforms, restrict content based on geographical location.
Avoid Censorship
Internet censorship is prevalent in some countries, where individuals may be monitored or content may be blocked.
How Do I Hide My IP Address?
There are several ways to hide your IP address. Here are options ranging from free, easy fixes to paid long-term solutions.
1. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
How it works:
A virtual private network (VPN) creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server run by the VPN provider. Any websites or apps you use see the VPN server’s IP address instead of your real one.
Pros
Protects your traffic from snooping on public Wi-Fi or by your ISP.
Lets you choose from servers around the world, great for bypassing geo-blocks (e.g., Netflix libraries abroad).
Works across most devices: computers, phones, tablets, and even routers.
Cons
Reliable services typically cost $5–$15/month.
Free VPNs may log your data or cap speeds.
Some sites (like banking apps) may flag logins from “unusual” IPs.
2. Proxy Servers
How it works:
A proxy sits between you and the internet. When you request a website, the proxy forwards the request on your behalf, masking your IP. Unlike VPNs, proxies usually don’t encrypt traffic.
Pros
Free and simple for one-off tasks (like checking region-blocked content).
Browser-based proxies require no installation.
Useful for light web browsing or testing website appearances in other regions.
Cons
Doesn’t encrypt your data, so your ISP or hackers on public Wi-Fi can still see it.
Free proxies are often overcrowded, slow, and unreliable.
Not suitable for sensitive activities like banking or shopping.
3. Tor (The Onion Router)
How it works:
Tor routes your connection through multiple random servers (called relays) around the world, encrypting each “layer” like an onion. This makes tracing your activity back to your real IP extremely difficult.
Pros
Free to use via the Tor Browser.
Provides strong anonymity — widely trusted by journalists, whistleblowers, and activists in restrictive countries.
Community-driven and decentralized, so no single entity controls it.
Cons
Significantly slower than normal browsing because of all the relay hops.
Many streaming sites, banks, and even Google may block Tor traffic.
Not ideal for daily streaming, gaming, or video calls.
4. Public Wi-Fi
How it works:
When you hop on public Wi-Fi at a coffee shop, hotel, or airport, your device uses that network’s IP address instead of your home one.
Pros
Free and doesn’t require extra tools.
Good for masking your home IP temporarily.
Convenient if you’re traveling and need a quick change.
Cons
Extremely vulnerable to hackers — unencrypted Wi-Fi can expose your traffic.
Only hides your IP while you’re connected to that hotspot.
Not a reliable or private long-term option.
5. Mobile Hotspot / Cellular Data
How it works:
By disconnecting from your home Wi-Fi and using your phone’s mobile data or hotspot, your internet traffic uses your mobile carrier’s IP address instead.
Pros
Quick and easy to switch — no setup needed.
Handy for troubleshooting (e.g., to see if a website is blocked on your home network).
Gives you a temporary new IP when needed.
Cons
Eats into your mobile data plan and can be expensive for heavy use.
Doesn’t provide true anonymity — your carrier still logs activity.
Not secure unless paired with HTTPS or a VPN.
Disadvantages of Hiding Your IP Address
While hiding your IP address is useful, it’s not without trade-offs. Consider the following before using a VPN to hide your IP address:
- Reduced Speeds – VPNs and Tor can slow connections since data is routed through extra servers.
- Blocked Services – Some streaming sites and banks block traffic from known VPN or proxy servers.
- Reliability Issues – Certain tools may disconnect, briefly exposing your real IP.
- Legal Restrictions – In some countries, VPNs or proxies are illegal or discouraged.
- Malicious Tools – Some free services log or steal user data; choose providers carefully.
- Compatibility Problems – Not all tools work across every device or operating system.
- False Sense of Security – IP masking doesn’t stop cookie tracking or malware infections.
How Do I Change My IP Address?
Sometimes you don’t need to hide your IP address — you just want a new one. Changing your IP can refresh your online identity and may fix certain connection or access issues. Here are a few easy ways to do it:
- Restart your modem or router – For most users with dynamic IPs, disconnecting and reconnecting your internet will trigger your ISP to assign a new address.
- Manually assign a new IP – On Windows or Mac, you can go into your network settings and configure a new IP address.
- Use a different network – Connecting to public Wi-Fi, mobile data, or a friend’s network gives you a different IP automatically.
- Request one from your ISP – Some providers will issue a new IP if you ask, or they may offer a static IP option for an additional fee.
Changing your IP address gives you a fresh online identity, but unlike IP masking, it doesn’t provide anonymity. If privacy is your goal, a VPN or other IP-hiding method is the better choice.
Real-World Use Cases for Hiding Your IP Address
Understanding the technical reasons to hide your IP address is important, but it helps to see how it plays out in everyday life. Here are a few common scenarios:
1. Streaming While Traveling
Many streaming services restrict their libraries by country. For example, if you’re traveling abroad and want to access BBC iPlayer, Hulu, or your local Netflix library, hiding your IP with a VPN allows you to connect through a server in your home country. That way, you can watch the shows and movies you’re used to—no matter where you are.
2. Working Securely from Hotels or Cafés
Public Wi-Fi networks, like those in hotels or coffee shops, are convenient but often unsecured. Using a VPN not only hides your IP address but also encrypts your traffic. This is especially important if you’re handling sensitive information, logging into work accounts, or checking financial data on the go.
3. Avoiding Price Discrimination
Some travel booking sites and retailers adjust prices based on your location. By hiding your IP and connecting through a different region, you may be able to compare offers and avoid inflated prices. For example, airline tickets might cost less if you appear to be searching from another country.
4. Protecting Identity While Gaming
Online gamers can be targeted by “DDoS attacks” if their IP addresses are exposed. Hiding your IP can reduce this risk, keeping your connection stable and your personal information private during competitive play.
5. Accessing Restricted Content at School or Work
In some workplaces or schools, certain websites—like social media, streaming platforms, or even news sites—are blocked. Masking your IP through a VPN or proxy may let you bypass those restrictions, though you should always consider your organization’s rules before doing so.
Legal & Ethical Considerations When Hiding Your IP Address
Hiding your IP address is legal in most countries, especially when done for legitimate reasons like protecting your privacy, securing sensitive data, or accessing content while traveling. However, there are a few important caveats:
- Countries With Censorship
In nations with strict internet controls—such as China, Iran, or North Korea—the use of VPNs and other masking tools is heavily restricted or outright illegal. Connecting through these services could result in fines or legal penalties. - Using IP Masking for Illegal Activity
While hiding your IP address can help protect your privacy, it does not give you a license to break the law. Activities such as hacking, copyright infringement, or committing fraud remain illegal, regardless of whether your IP is hidden. - Workplace or Institutional Policies
Some schools, universities, and companies prohibit the use of VPNs or proxies on their networks. Circumventing these policies could result in disciplinary action.
Disclaimer: Always check your local laws and institutional rules before using tools that hide your IP address. Using these tools responsibly ensures you benefit from added privacy and security without unintended consequences.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Online Privacy
Hiding your IP address is a practical step toward protecting your privacy, securing your data, and expanding what you can access online. Whether you use a VPN, a proxy, Tor, or even a quick switch to mobile data, each method offers its own balance of convenience, speed, and security.
For most people, starting with a reputable VPN provides the best mix of protection and usability. From there, pairing it with a secure and reliable browser, strong passwords, and other cybersecurity tools will give you a well-rounded defense against today’s online risks.
By understanding your options and choosing the right approach, you can take back control of how—and where—your digital footprint appears.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hiding Your IP Address
No. Incognito or private browsing mode only prevents your browser from saving history, cookies, and cache. It does not mask your IP address. Websites, your ISP, and network administrators can still see your IP unless you use IP masking tools like a VPN or proxy.
You can hide your IP address with several methods, including VPNs, proxy servers, the Tor browser, public Wi-Fi, or mobile data. VPNs are the most reliable because they not only hide your IP but also encrypt your traffic for added security.
Yes, your IP address can reveal your approximate location and your internet service provider. While it usually can’t pinpoint your exact street address on its own, it can still be used for tracking, targeted ads, or malicious attacks if exposed.
Hiding your IP address means masking it behind another address (e.g., through a VPN or proxy), so websites can’t see your real one.
Changing your IP address means requesting or receiving a new one (e.g., resetting your router, contacting your ISP, or switching networks). Both methods protect privacy, but hiding offers stronger anonymity.
It depends on your needs. If you’re concerned about online privacy, streaming restrictions, or security, hiding your IP address at home is useful. However, for casual browsing on a secure network, it may not be strictly necessary.
The main benefits include:
- Improved online privacy and reduced tracking
- Protection from hackers and cybercriminals
- Access to geo-restricted content like streaming libraries
- Avoiding price discrimination on travel or shopping sites
- Added anonymity when browsing or gaming
Hiding your IP address helps safeguard your personal information, prevent unwanted tracking, and give you more control over your online experience. It’s a simple step toward stronger cybersecurity and online freedom.
In most countries, using tools like VPNs (virtual private network) or proxies is legal when done for legitimate reasons such as privacy or security. However, in countries with strict censorship laws, VPNs and other IP masking methods may be restricted or illegal. Always check local regulations before using these tools.
The easiest way is to check your IP address before and after using an IP masking tool. You can do this by typing “what is my IP address” into Google or visiting a site like whatismyip.com. If the address displayed changes when you connect through a VPN, proxy, or Tor, then your real IP is hidden. For extra assurance, make sure the displayed location also matches the server or region you selected in your tool.