HighSpeedOptions prides itself on providing honest, quality content. While we may be compensated when you make a purchase through links on our site, all opinions are our own. Here's how we make money.
The average VPN has at least a couple of VPN protocols to offer, but what’s the difference between the likes of OpenVPN and IPsec, and will there be an impact on performance for the average user?
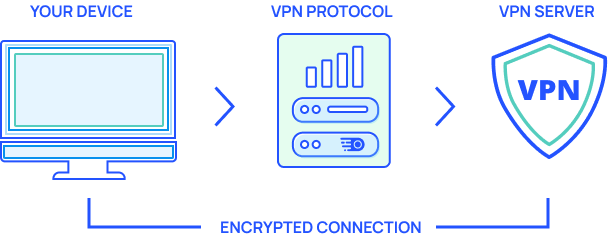
What Is a VPN Protocol?
A virtual private network (VPN) protocol is a set of instructions that are used to transmit your online traffic safely, often while assigning the user with a new IP address. There are many protocols available, from famous open-source options to proprietary, specific-use protocols.
The type of protocol used will have an impact on aspects such as internet speed and security. You can guess that this is especially important for the end-user. Combined with the base speeds offered by your internet providers, this is especially important for the end-user.
For simplicity, here are the most common VPN protocols in use today.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN was created and released in 2001 by James Yonam, who is the current CTO of OpenVPN Inc. It earns the name due to being open-source, and it’s available on all major platforms and comes with strong industry recommendations.
OpenVPN uses OpenSSL for encryption and authentication, with a choice between UDP (User Datagram Protocol) or TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) for transmitting the data to and from your device.
The main difference between the two is that UDP is faster. Although, it’s more likely to encounter errors due to lost data packets. This means that TCP is often preferred unless it’s for an intensive task such as online gaming.
Pros
Open-source software licensed under GNU GPL
Widely accepted as one of the most secure protocol options while using TCP
Free to download and use so long as you can configure it or your VPN offers it outright
Cons
Slightly dated compared to modern releases
Not the fastest protocol, but it’s available with most commercial VPN apps
Requires third-party software and certificate files to be installed
L2TP
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) supports VPN networks but lacks encryption. To enhance privacy, it’s commonly used alongside IPsec, forming the combination known as L2TP/IPsec.
L2TP/IPsec verifies transmitted data twice, impacting connection speeds. However, it offers robust security measures compared to other protocols. It serves as the successor to PPTP, which we discuss later.
Pros
Widely compatible with the majority of platforms and operating systems
Uses AES-256 bit encryption
L2TP/IPsec is a solid combination for encryption and authentication
Cons
L2TP/IPsec uses UDP port 500 which is easily detected and blocked by firewalls
L2TP on its own is not very useful
Not as widely available across premium VPN providers
IPsec
IPsec is a protocol utilized to ensure the security of data transmitted across public networks. It achieves this by encrypting IP packets and verifying the integrity of the transmitted data. The acronym “IP” refers to “Internet Protocol,” while “sec” denotes “secure.”
To bypass firewalls, IPsec employs UDP, facilitating the passage of IPsec packets. It operates in either Transport mode or Tunnel mode, with the latter being the default mode. Tunnel mode encrypts the entire data packet, while Transport mode is well-suited for secure communications.
In addition to L2TP, IPsec can be combined with other protocols such as IKEv2, as discussed later on. Moreover, it can function as a standalone solution for Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
Pros
Solid authentication
Known for its robust network security
Available via transport mode or tunnel mode
Cons
IPsec will have an impact on speeds and performance while in use
There are potential restrictions due to firewall issues
IPSec has an inconsistent standard for its own compatibility
SSL/TLS
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is utilized to encrypt data packets, ensuring a secure connection within the browser. SSL certificates also help in establishing a reliable connection with the correct server.
Initially released in 1994 by Netscape Communications Corporation, SSL aimed to enhance web session security. The Transport Layer Security protocol (TLS) succeeded SSL and is now widely adopted by modern VPN services. Introduced in 1999, TLS was developed to address severe security vulnerabilities discovered in SSL.
Although SSL and TLS are oftentimes used interchangeably, it is mostly TLS that is being referred to. (TLS v1.0 was initially developed as SSL v3.1, which explains the frequent confusion between the two terms.)
Pros
An SSL VPN provides end-to-end encryption between the VPN client and its servers
SSL used in online payment authentication due to its high security
Google algorithm prefers SSL over other authentication methods to rank pages
Cons
An SSL VPN will actually use TLS due to serious security flaws found within the protocol
OpenVPN is an example of an SSL VPN, so it’s not compatible with IPsec or L2TP
Not as commonly used by VPN providers as OpenVPN or IKEv2
SSTP
Initially created by Microsoft as a proprietary choice, SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol) leverages an SSL/TLS channel. It made its debut with the introduction of Windows Vista. SSTP boasts effortless firewall evasion capabilities and enables access to restricted content. Due to its Windows-centric design, it is not the most compatible option.
Pros
Seen as a more secure alternative to the likes of PPTP or L2TP/IPsec for Windows
SSTP may offer similar speeds and security to OpenVPN
Helps bypass firewalls better than other protocols
Cons
Being solely owned by Microsoft isn’t ideal from a privacy perspective
Can have an impact in terms of connection speeds while the VPN is active
Not ideal for non-Windows software like Linux or macOS
PPTP
Point-to-point tunneling protocol (PPTP), the elder sibling of SSTP, dates back to the Windows ’95 era, and is now obsolete. We strongly advise against using it, except for situations where you need to access faster speeds on outdated hardware or have no other protocol options available. It is important to note that PPTP is prone to various known vulnerabilities due to its weak encryption.
Pros
It’s a fast protocol option, especially on older devices
Native built-in support for many popular operating systems including Windows, Android, MacOS and iOS
Fairly easy to set up on devices if not offered by VPN provider outright
Cons
Obsolete, because of various security vulnerabilities
Many issues stem from Challenge/Response Authentication Protocol (CHAP), or inadequate hashing algorithms
Less reliable compared to SSTP since it lacks data origin verification and data integrity process
WireGuard
WireGuard, an acclaimed protocol, is a newer encryption solution that offers simplicity, enhanced security, and easier auditability. Developed by Jason A. Donenfeld, a prominent cryptographer at Edge Security, WireGuard saw its first stable release, version 1.0.0, on March 29, 2020.
With its exceptional speed, WireGuard is often used in speed tests for reviewing purposes. However, it is currently considered an experimental protocol and has yet to be widely adopted by providers.
Pros
One of the fastest protocols overall, making it great for streaming and torrenting
Roughly 4,000 lines of code vs OpenVPN’s 70,000 lines of code
Strong encryption, with no known security flaws
Cons
Only a handful of premium VPNs offer it as its so new
Security concerns as it hasn’t been vetted as long as protocols like OpenVPN
It requires separate servers, distributions, and key management, which is another hurdle to VPN providers supporting this protocol
IKEv2
IKEv2, commonly used alongside IPsec, is a favored solution that strikes a perfect balance between rapid connection speeds and robust encryption. Originally a collaboration between Microsoft and Cisco, it presented a significant upgrade to the Internet Key Exchange back in 2005.
With a Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm and support for AES 256-bit encryption, IKEv2/IPsec ensures strong security without any known vulnerabilities. Offering stability and quicker performance compared to its counterparts, it stands out in the competition.
Pros
IKEv2 is one of the faster protocols available considering the level of encryption
Typically used with IPsec, another reputable protocol for privacy
Good stability, and deployed by many commercial providers
Cons
Easier to block with the use of firewalls due to the use of UDP port 500
Offers limited support for devices outside the Windows and Apple ecosystems
ome open-source versions exist, but it’s primarily a close-sourced development of Microsoft and Cisco
Additional Proprietary Protocols
As the name suggests, proprietary protocols are typically developed and used by a single company, or in some cases are licensed out for further use. They claim that it gives them an edge over the competition listed above, as it will have been specifically designed to work with their network.
Lightway is a very new VPN protocol released by ExpressVPN in the summer of 2021. They note that, “nine out of ten beta users reported that Lightway got them connected to the VPN faster than before.”
Another example would be Catapult Hydra by Hotspot Shield and its parent company, AnchorFree. According to them, “AnchorFree used to use standard IPSec and OpenVPN protocols to power Hotspot Shield but found major performance and latency challenges with it, therefore we created our own proprietary Catapult Hydra to address the issues of VPN latency.”
There’s also NordVPN’s repackaged version of WireGuard that they branded as NordLynx. They claim that with it, users can “experience WireGuard’s speed benefits without compromising your privacy.”
Pros
Proprietary protocols tend to be responsive as they were designed solely for the VPN service
They’re still a worthy additional feature and are always worth testing out
Specialty protocols can be very attuned to specific use cases
Cons
Many are still in beta mode, and may not be as stable as other options
Expect VPN services to embellish the results of their tests ever so slightly. (It’s unlikely that speeds will be many times faster than using an OpenVPN/WireGuard/IKEv2 solution.)
Rarely available outside the VPN service which it was created for and by
Best Protocol for Speed
Speed is key to accessing content without lag or buffering, and it’s one of the most important aspects for the average VPN user. To this end, it’s hard to look past proprietary options that have been custom-built for the job at hand.
IKEv2 should be a little faster than OpenVPN, while the barebones nature of PPTP also makes it speedy. WireGuard is a great protocol, but we recognize that it’s still in development.
Overall, The best protocol for speed depends on the task at hand, as well as your typical internet speeds, and the provider selected. Surfshark is our pick for best VPN for streaming thanks to P2P support, while CyberGhost has a massive high-speed server network.
Best Protocol for Privacy
Online privacy is often disregarded in favor of features like access to streaming services, but it’s becoming ever more important as multiple companies compete for our personal data.
The best protocol for privacy has to be OpenVPN at this moment in time, as it’s the industry standard for a reason. IKEv2 is a great pick for the strongest encryption and security, although it’s worth mentioning that WireGuard has no known major vulnerabilities.
We’d couple the use of OpenVPN/NordLynx with NordVPN for the best results in terms of security and privacy. IPVanish also has robust security features. Further options include ProtonVPN, while Mullvad is an audited privacy-focused service that uses OpenVPN and WireGuard for tunneling.
Best Protocol for Compatibility
What if you plan to use a protocol across different devices, and a range of operating systems? The ideal protocol for compatibility has to be OpenVPN, given it’s a solid option that can be used across a wide range of apps and devices. In comparison, WireGuard is great, but it’s not readily available with many VPN services.
However, the “best protocol” might be dependent on the VPN provider you’ve selected, as they are likely to have various options that differ depending on the platform.
For example, NordVPN offers OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPsec, and WireGuard via NordLynx, with their proprietary protocol used as the recommended setting.
IPVanish has the following protocols available including IKEv2, OpenVPN, L2TP, IPsec, and PPTP. (OpenVPN works with every operating system, whereas WireGuard is only available for Windows, iOS, macOS, Android, and Fire TV.) To access Chrome with IPVanish, you’ll have to use OpenVPN or L2TP.
Best Protocol for Content
Isn’t the best VPN protocol for streaming the same as the best VPN protocol for speed? Not necessarily, as it’ll be more dependent on whether the VPN is able to access content like US Netflix in the first place. They will also need local servers in the location you would like to connect to, and a constant list of new IPs. Protocol selection will have an impact on speeds, and the same is true for streaming and torrenting.
Final Thoughts
Clearly, the protocol selected will have a major impact on a VPN’s performance and security. Some protocols are now obsolete, offering poor levels of encryption that are easily cracked, while others are still in the development stage but make for viable options in the long term.
Ideally, a VPN provider will have a large selection of protocols to select from within its app, giving the user the opportunity to decide which is best for any given scenario. At the very least, OpenVPN and IKEv2/IPsec should be included as standards.